Распространенность патологической инвазии плаценты в исследованиях, опубликованных в период с 1982 по 2018 гг., варьирует от 1:100 до 1:10 000 родов [1]. За последние несколько десятилетий заболеваемость, связанная с патологической инвазией плаценты, значительно увеличилась, что связано с увеличением удельного веса кесарева сечения [2, 3].
Массивное интраоперационное кровотечение и кровотечение в послеродовом периоде, являясь наиболее частыми осложнениями патологической инвазии плаценты, могут привести к еще более грозным состояниям, таким как диссеминированное внутрисосудистое свертывание крови, полиорганная недостаточность, шок и даже летальный исход. Гистерэктомия и повреждение смежных органов (мочевыводящих путей, кишечника) являются другими распространенными осложнениями, которые могут влиять на качество жизни женщины, ее физическое и психическое здоровье [4, 5].
Для предотвращения тяжелых осложнений и выбора оптимальной акушерской тактики необходимо своевременно диагностировать патологическую инвазию плаценты.
Плацентация – сложный процесс, требующий миграции вневорсинчатого трофобласта, который дифференцируется в интерстициальные и эндоваскулярные субпопуляции [6]. Интерстициальные трофобласты проникают в децидуальную оболочку матери, а эндоваскулярные трофобласты проникают в спиральные артерии матери. При здоровой беременности трофобластическая инвазия и ангиогенез хорошо сбалансированы вместе с защитным барьером материнской децидуальной оболочки. Однако при врастании плаценты инвазия трофобласта проникает за децидуальный слой [7]. По глубине инвазии трофобласта врастание плаценты можно разделить на следующие три категории: placenta accreta, placenta increta, placenta percreta. Данная градация недавно очень полно была представлена Международной Федерацией гинекологии и акушерства (FIGO) и Обществом акушеров-гинекологов Канады [8, 9].
Чрезмерная инвазия трофобласта вместе с децидуальной недостаточностью являются основными механизмами, определяющими патофизиологию патологической инвазии плаценты [10].
Наряду с дисбалансом внутри этих хорошо известных процессов обращает на себя внимание еще один фактор – распространенная маточно-плацентарная неоваскуляризация в зонах врастания плаценты. Между микросредой патологически инвазивной плаценты и патофизиологией опухоли можно провести ряд сравнений. Оба состояния требуют от клеток способности преодолевать локальный иммунологический барьер, активировать инвазию и индуцировать неоангиогенез. Кроме того, между опухолевым процессом и врастанием плаценты существуют отличительные особенности, заключающиеся в глубине инвазии, степени эпителиально-мезенхимальной трансформации и способности к метастазированию [11–14].
Ультразвуковая диагностика
В настоящее время визуализация является основным методом предоперационной диагностики патологической инвазии плаценты в клинической практике. Широко используются ультразвуковое исследование (УЗИ) и магнитно-резонансная томография (МРТ). УЗИ имеет преимущества в отношении безопасности, экономичности, скорости и удобства и является наиболее широко используемым методом диагностической визуализации в клинической практике. Несмотря на большое количество исследований различных ультразвуковых маркеров врастания плаценты и эффективности их диагностических возможностей, сохраняются некоторые противоречия в трактовке основных и дополнительных ультразвуковых критериев патологической инвазии плаценты в современной литературе.
В связи с необходимостью стандартизации в определении ультразвуковых маркеров врастания плаценты рабочими группами экспертов Международного общества ультразвука в акушерстве и гинекологии, Общества радиологов в области ультразвука и других организаций в 2021 г. был осуществлен поиск консенсуса относительно единых подходов к пренатальной ультразвуковой оценке матки и плаценты у беременных с риском приращения плаценты [15].
Консенсус ультразвуковых специалистов в акушерстве и гинекологии определил, что в настоящее время УЗИ является основным методом скрининга врастания плаценты [16]. Консенсусом было признано отсутствие согласия в отношении оптимального срока беременности для диагностики признаков врастания плаценты и различия в подходах к ультразвуковой оценке плаценты [17]. Особо подчеркивается, что некоторые клинико-анамнестические факторы риска, такие как наличие рубца на матке, предлежание плаценты, частые внутриматочные вмешательства и прочее, оказывают значительное влияние на положительную прогностическую оценку сонографических маркеров в отношении врастания плаценты; в то же время, как показали недавние исследования, все эти факторы могут присутствовать в равной степени и у женщин с низким риском патологической инвазии плаценты [18].
Ультразвуковые маркеры патологической инвазии можно увидеть уже в середине I триместра беременности, хотя исторически скрининг на врастание плаценты принято проводить во II и III триместре [19]. Одним из основных ультразвуковых признаков, определяющих прогноз патологической инвазии плаценты, служит беременность, которая локализуется в нише рубца на матке. Беременность в рубце на матке – это разновидность внематочной беременности, при которой бластоциста имплантируется в зону ниши рубца. Это самая редкая форма внематочной беременности, составляющая 0,4% всех беременностей и 6% всех внематочных беременностей у пациенток с предшествующим кесаревым сечением в анамнезе [20, 21].
Установлено, что существуют различия в распространенности и типе патологических маркеров, определяемых по данным УЗИ, в середине I триместра беременности (6–9 недель гестации) и в более позднем периоде I триместра (11–14 недель гестации) [22].
В начале I триместра можно оценить положение плодного яйца по отношению к рубцу на матке и зарегистрировать низкую или среднюю по расположению имплантацию плодного яйца (тип 1 и тип 2). Низкую имплантацию (тип 1) плодного яйца диагностируют, когда нижний край плодного яйца находится в пределах или в непосредственной близости от рубца на матке и/или имплантация происходит в правильно заживший рубец (поверхностная рубцовая беременность). Средняя имплантация (тип 2) определяется, когда плодное яйцо имплантируется в нише рубца на матке (глубокая рубцовая беременность), образованной предыдущим расхождением рубца. Во втором случае прогноз хуже, чем при имплантации в сам рубец [23–25].
Нишу следует определять, как углубление на месте рубца на матке глубиной не менее 2 мм. Нишу рубца на матке классифицируют следующим образом: 1) простая ниша; 2) простая ниша с одной ветвью; 3) сложная ниша (с более чем одной ветвью). Полагают, что ветвь является более тонкой частью основной ниши, поскольку она направлена в сторону серозной оболочки матки и имеет ширину меньше, чем у основной ниши.
Клинически значимые измерения ниши включают длину, глубину, остаточную толщину миометрия, ширину, прилегающую толщину миометрия, расстояние между нишей и внутренним зевом цервикального канала (рис. 1) [26].
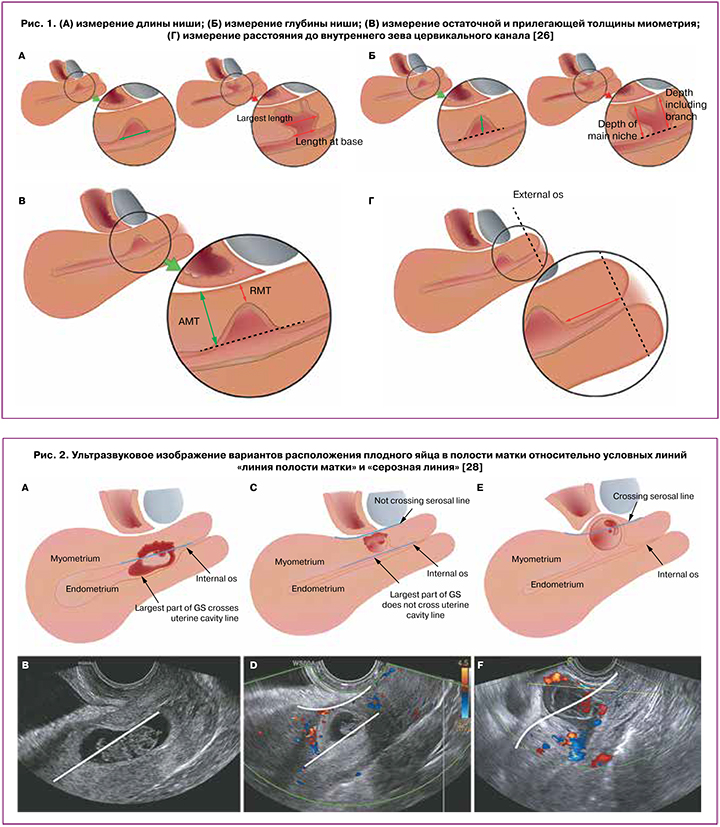
Длина, глубина, остаточная толщина миометрия, прилегающая толщина миометрия, расстояние между нишей и внутренним зевом цервикального канала должны измеряться в сагиттальной плоскости, а поперечная плоскость считается актуальной только для измерения ширины ниши и идентификации ответвлений [26].
Следующие критерии ультразвуковой диагностики рубцовой внематочной беременности освещены в современной литературе [27–29]:
1) отсутствие плодного яйца в полости матки и четко визуализируемый эндометрий;
2) отсутствие плодного яйца в цервикальном канале;
3) плодное яйцо, имплантированное в нижний передний сегмент матки в предполагаемом месте рубца после кесарева сечения;
4) треугольная форма до 8-й недели беременности и округлая или овальная форма плодного яйца после 8-й недели беременности, которое заполняет «нишу»;
5) тонкий или отсутствующий слой миометрия между мочевым пузырем и плодным яйцом (в большинстве случаев менее 5 мм, чаще 1–3 мм);
6) отчетливый и богатый сосудистый рисунок вокруг области рубца.
По мнению экспертов по ультразвуковой диагностике, длина, ширина, глубина «ниши» не имеют прогностического значения в отношении врастания плаценты, так как данные параметры изменяются с течением беременности.
Одним из важнейших прогностических ультразвуковых критериев для оценки риска инвазии плаценты является положение плодного яйца относительно двух условных линий, а именно пересекает ли плодное яйцо две воображаемые линии: «линия полости матки» и/или «серозная линия» (рис. 2) [28].
Установлено, что данное описание имеет 3 градации: первая, при которой больший диаметр плодного яйца пересекает линия полости матки; вторая, при которой большая часть плодного яйца встроена в миометрий и не пересекает зону эндометрия; третья, при которой плодное яйцо пересекает серозную линию [28]. Неблагоприятными в отношении рисков инвазии плаценты принято считать второй и третий типы расположения плодного яйца.
Стоит отметить, что низкое расположение плодного яйца в ранние сроки I триместра беременности при подтвержденных случаях патологической инвазии плаценты встречается практически в 100%, а в конце I триместра оно выявляется примерно у 28% [22].
Чтобы обеспечить максимальную пользу от первичной диагностики в I триместре беременности и выбрать оптимальную тактику (выжидательную или активную), необходимо всем беременным с рубцом на матке после кесарева сечения в анамнезе проходить ультразвуковой контроль в стационарах третьего уровня с привлечением экспертов в данной области [30].
Двухмерное (2D) УЗИ в оттенках серого и цветная допплерография во II и III триместрах также являются рекомендуемыми методами визуализации для диагностики патологической инвазии плаценты [17]. Классические сонографические маркеры врастания плаценты включают в себя следующие: наличие плацентарных лакун, потеря ретроплацентарной гипоэхогенной зоны, гиперваскуляризация маточно-пузырного или ретроплацентарного пространства, распространение плацентарной ткани в матку или мочевой пузырь, плацентарные мостиковые сосуды [16].
Плацентарные лакуны часто описываются, как крупные и неравномерные анэхогенные образования в паренхиме плаценты. В некоторых отчетах лакунарный кровоток описывается, как низкоскоростной, в других сообщается о турбулентном высокоскоростном потоке [16].
Finberg H.J., Williams J.W. в своей основополагающей работе 1992 г. по ультразвуковым маркерам патологической инвазии плаценты предложили классификацию плацентарных лакун в сосудистом пространстве, где степень 0 указывает на отсутствие плацентарных лакун, степень 1 включает 1–3 маленькие лакуны, степень 2 содержит от 4 до 6 более крупных и нерегулярных лакун и степень 3 описывает плаценту со множеством больших и «странно выглядящих» лакун по всей поверхности [31].
Аномальный маточно-плацентарный интерфейс был описан, как потеря ретроплацентарной гипоэхогенной зоны, истончение миометрия и повышенная васкуляризация при цветном допплеровском исследовании [32]. Классическим определением истончения миометрия является ретроплацентарная толщина миометрия менее 1 мм. Оно часто наблюдается на ранних сроках беременности и может быть более выраженным у женщин, перенесших кесарево сечение в анамнезе [33].
Маркеры уретеро-везикального интерфейса включают мостиковые сосуды, повышенную васкуляризацию между маткой и мочевым пузырем и разрыв стенки мочевого пузыря. Сосуды-мостики представляют собой неоваскуляризацию поверх серозной оболочки матки и часто в пределах маточно-везикального пространства [22, 34]. Гиперваскуляризацию маточно-пузырной поверхности отражают расширение маточно-плацентарной сосудистой сети и хаотический рост сосудов в этом пространстве [34]. Варикозное расширение вен мочевого пузыря часто наблюдается при отсутствии врастания плаценты и при предлежании плаценты, что подчеркивает сложность оценки этого маркера [16]. Прерывание эхогенной линии стенки мочевого пузыря, особенно плацентарной тканью, является четким маркером инвазивного процесса, поскольку представляет собой распространение плацентарной ткани за пределы матки [34].
В литературе описан ряд иных ультразвуковых маркеров, позволяющих предполагать патологическую инвазию плаценты: визуализация маточной грыжи в виде отклонения/выпячивания серозной оболочки матки в сторону от ожидаемых плоскостей, в том числе в мочевой пузырь, расширение сосудов шейки матки. Первые два с большой вероятностью указывают на врастание плаценты, в то время как последний работает плохо, поскольку он был идентифицирован более чем в 50% случаев без патологической инвазии [32, 34, 35].
Rac M.W. et al. применили многопараметрический анализ с использованием различных сонографических и клинических признаков для эффективной диагностики риска патологической инвазии плаценты [36]. Был предложен индекс вероятности, названный индексом PAI (патологическая аномальная инвазия).
Эта модель представляет собой 9-балльную систему оценки с использованием 5 параметров УЗИ, определенных как маркеры для пренатальной диагностики патологической инвазии плаценты. Параметрами, включенными в PAI, являются количество предшествующих операций кесарева сечения, расположение плаценты, лакунарная градация, наличие мостиковых сосудов и наименьшая толщина миометрия при измерении в сагиттальной плоскости. При значении PAI <5 риск патологической инвазии оценивается как низкий, при PAI >5 – как высокий. Если параметр отсутствует, то значение равно 0 [36–39]. Значение каждого параметра представлено ниже (таблица).

В недавнем исследовании китайских ученых описан так называемый «рельсовый признак», который сочетает в себе повышенную васкуляризацию слизистой оболочки мочевого пузыря, субплацентарную или маточно-везикальную гиперваскуляризацию и наличие мостиковых сосудов, при верификации которых в 5 раз увеличивается риск глубокой инвазии плаценты [40].
Магнитно-резонансная томография
Ультразвуковое цветное допплеровское картирование является методом визуализации патологической инвазии плаценты первой линии [41], однако МРТ играет дополнительную роль в антенатальной диагностике патологической инвазии плаценты. По сравнению с ультразвуком, МРТ имеет преимущества мультисрезового многонаправленного объемного изображения, большего поля зрения, высокой контрастности мягких тканей и пространственного разрешения, а также не зависит от влияния кишечного газа и толщины брюшной стенки [42, 43].
В 2020 г. Обществом абдоминальной радиологии (SAR) и Европейским обществом урогенитальной радиологии (ESUR) был принят консенсус о стандартах МРТ-диагностики при врастании плаценты. В нем были предложены стандартизированный протокол визуализации и система отчетности, обеспечивающая распознавание существенных признаков патологической инвазии плаценты. Был предложен общий словарь терминов, позволяющий обеспечить единообразие в получении и интерпретации результатов исследования при врастании плаценты при МРТ. Выделено 7 маркеров МРТ, а именно внутриплацентарные темные полосы на Т2-взвешенном изображении, патологическое выпячивание матки/плаценты, потеря ретроплацентарной линии сигнала низкой интенсивности на Т2-взвешенном изображении, истончение/разрыв визуализации миометрия, прерывистость контуров стенки мочевого пузыря, фокальная экзофитная плацентарная масса и аномальная сосудистая сеть плацентарного ложа [44].
Остановимся подробнее на данных критериях.
1. Темные внутриплацентарные полосы на T2-взвешенном изображении определяются как узелковые или линейные области с низкой интенсивностью сигнала, имеют неровные края и максимальный диаметр от 6 до 20 мм и более. Считается, что они представляют собой области отложения фибрина из-за повторяющихся внутриплацентарных кровотечений или инфарктов [45]. По результатам метаанализа Sentilhes L. et al., наличие аномальных внутриплацентарных темных полос является наиболее чувствительным МРТ-признаком для диагностики врастания плаценты [46, 47].
2. Визуализация маточной грыжи, определяемой как очаговое выпячивание внешнего контура или нарушение нормальной грушевидной формы матки, при этом нижний сегмент матки шире дна [46]. Аномальное выпячивание имеет превосходную точность и тесно связано с наличием placenta increta и percreta [48].
3. Потеря ретроплацентарной гипоинтенсивной линии на T2-взвешенных изображениях. В зонах патологической инвазии плаценты могут наблюдаться очаговая прерывистость слоев матки или утрата этого интерфейса [44].
4. Если миометрий хорошо выражен, то в местах инвазии плаценты видны фокальные разрывы контура стенки матки плацентарной тканью. В метаанализе Bourgioti C. et al. установлено, что чувствительность признака очагового прерывания контура миометрия в диагностике placenta percreta составляет 78,6%, однако при placenta increta и accreta чувствительность этого признака была существенно меньше [47, 49].
5. Прерывистая визуализация, неравномерность или «втяжения» стенки мочевого пузыря позволяют заподозрить инвазию плаценты в эту область. Прямая визуализация плацентарной ткани в просвете мочевого пузыря на МРТ является высокоспецифичной (100%) в отношении поражения мочевого пузыря, однако эта особенность наблюдается только у небольшого числа пациентов с placenta percreta [49]. Признак наличия сосудов в зоне мочевого пузыря, определяемый как визуализация многочисленных извилистых сигнальных пустот, пересекающих пространство от матки до мочевого пузыря, является еще одним точным предиктором поражения стенки мочевого пузыря (включая серозную оболочку мочевого пузыря) с высоким уровнем чувствительности до 96% [49].
6. Очаговая экзофитная масса, определяемая как плацентарная ткань, которая прерывает серозную оболочку матки и выходит за ее пределы, чаще всего наблюдается внутри наполненного мочевого пузыря. Этот признак характерен только для случаев placenta percreta [47].
7. Аномальная внутриплацентарная васкуляризация, при которой сосудистая архитектура плацентарного ложа претерпевает значительные изменения. При этом сосуды становятся неравномерно распределенными и очень гетерогенными по структуре. Чем агрессивнее протекает процесс аномальной инвазии плаценты, тем более выражены маточно-плацентарные сосудистые изменения.
Исследование Konstantinidou A.E. et al. (2019) выявило аномальный внутриплацентарный сосудистый рисунок именно в зоне патологической инвазии плаценты и продемонстрировало эмбриональное происхождение этих сосудов [50]. Авторы утверждали, что эти аномальные сосуды представляют собой расширенные субхориальные сосуды, берущие начало от пуповины и впадающие вглубь паренхимы плаценты, нередко достигая ее материнской поверхности. Нормальные плацентарные сосуды плода становятся незаметными вскоре после того, как они входят в плаценту, но при патологической инвазии плаценты эти сосуды более удлинены и имеют больший диаметр с недостаточным разветвлением, окружены разреженной тканью хориона, по сравнению с нормальными сосудами плаценты (патологический признак полосатого сосуда плода) [50].
Исследование, проведенное в 2021 г., сообщает о том, что наличие одного или нескольких внутриплацентарных сосудов плода диаметром 2 мм и более глубоко внутри плаценты является точным и независимым МРТ-предиктором врастания плаценты, а наличие внутриплацентарных сосудов плода диаметром 3 мм и более прогнозирует наличие placenta percreta и осложненное течение послеродового периода [51].
Этот признак является важным критерием различия между placenta percreta и placenta accreta/increta [46, 52]. Установлено, что наличие гиперваскуляризации серозной оболочки матки на пренатальной МРТ прогностически связано с повышенной интраоперационной кровопотерей и необходимостью пластики мочевого пузыря [14 ,42, 52].
Все вышеописанные маркеры характерны для предлежания плаценты и признаков ее врастания по передней стенке [53]. Поэтому предсказать патологическую инвазию при расположении плаценты преимущественно по задней стенке достаточно трудно [54, 55].
Ряд авторов сообщают о возможности прогноза врастания плаценты по задней стенке [56]. Таким параметром послужило варикозное расширение сосудов шейки матки, но исследований данного вопроса очень мало.
Эластография
Патологические процессы могут проявляться изменением эластичности тканей. Изменения жесткости тканей под влиянием физиологических или патологических факторов в тканевой структуре выявляются раньше, чем их клинические признаки. В настоящее время различные методики эластографии с возможностью оценки механических свойств ткани позволяют выявлять и контролировать различные патологические состояния вне беременности, при здоровой беременности или беременности, сопровождающейся различной патологией [57–64], в том числе патологическое состояние плаценты, в частности патологическую инвазию плаценты [65–67].
Различные методы эластографии, доступные в настоящее время, могут быть разделены на визуализацию деформации и визуализацию сдвиговой волны (SWI) в соответствии с измеряемой величиной [68].
Сам процесс ультразвуковой эластографии можно представить следующим образом: сначала к ткани-мишени прикладывают механическое воздействие, а затем получают смещение или поперечную сдвиговую волну, генерируемую тканью-мишенью. Далее эти сигналы улавливаются и отображаются соответствующими параметрами [69]. В настоящее время клинические визуализирующие методы диагностики в основном включают компрессионную эластографию, транзиентную эластографию, акустическую лучевую импульсную визуализацию, измерение скорости поперечной сдвиговой волны и визуализацию с использованием импульсного возбуждения силы акустического излучения [70].
В компрессионной эластографии методы стимуляции включают ручное сжатие ткани оператором с помощью ультразвукового преобразователя или генерируемое внутренними физиологическими движениями, такими как сердечно-сосудистая или дыхательная система. Однако искусственное или физиологическое давление не может быть определено количественно, что требует навыков и опыта оператора для многообещающих результатов [71].
Новый метод эластографии, который может анализировать жесткость тканей качественно и количественно, – акустическая лучевая импульсная визуализация (Acoustic radiation force impulse визуализация (ARFI)). ARFI оценивает жесткость ткани, обеспечивает дополнительной информацией при традиционной ультрасонографии; таким образом, потенциально улучшает возможность описания характеристик тканей и очаговых поражений [66].
В настоящее время ARFI – новейший режим визуализации для обнаружения механических свойств ткани без применения внешнего сжатия. ARFI включает в себя 2 режима – виртуальное изображение ткани (Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging, VTI) и виртуальную количественную оценку эластичности ткани (Virtual Touch Tissue Quantification, VTQ) [72].
Mикросмещение генерируется в ткани в пределах интересующей области с помощью ультразвукового датчика, который запускает в ткани кратковременные акустические импульсы (<100 мс) высокой интенсивности. Смещение ткани зависит от ее эластичности. Чем более эластичная ткань, тем больше она подвергается смещению. Смещение ткани внутри поля зрения, вызванного ARFI, регистрируют и представляют как полутоновое изображение, которое называется VTI. Чем плотнее ткань, тем темнее изображение [66, 72].
Ткани в пределах поля зрения генерируют горизонтальное смещение волны вследствие распространения продольного импульса, генерируемого датчиком. Скорость сдвига волны рассчитывается и выражается в единицах м/с, что называется VTQ. Чем плотнее ткань, тем быстрее распространяются волны. Скорость распространения волны является внутренним и воспроизводимым параметром самой ткани, так что ARFI ткани выдает объективные и воспроизводимые данные. VTQ обеспечивает числовые измерения скорости сдвига волны, а сама скорость сдвига волны пропорциональна квадратному корню из эластичности ткани, поэтому VTQ – количественная технология оценки эластичности ткани.
ARFI впервые была применена в диагностике заболеваний брюшной полости, молочной железы и щитовидной железы [72]. Публикаций о применении технологии ARFI при патологической инвазии плаценты, особенно с использованием линейного датчика, немного, и эта проблема по-прежнему требует дальнейшего исследования.
Заключение
Таким образом, основными ультразвуковыми маркерами патологической инвазии плаценты в I триместре являются: визуализация плодного яйца в нише рубца на матке (2-й тип имплантации), 2-й и 3-й типы расположения плодного яйца в полости матки, при которых, соответственно, большая часть плодного яйца встроена в миометрий и не пересекает зону эндометрия, либо плодное яйцо пересекает условную серозную линию. Классическими признаками патологической инвазии плаценты во II и III триместрах следует считать наличие плацентарных лакун, потерю ретроплацентарной гипоэхогенной зоны, гиперваскуляризацию маточно-пузырного или ретроплацентарного пространства, распространение плацентарной ткани в миометрий или мочевой пузырь, плацентарные мостиковые сосуды. Дополнительными признаками следует считать повышенную васкуляризацию мочевого пузыря или маточно-везикального пространства. Интегральная оценка индекса врастания плаценты может быть полезной для диагностики ее аномальной инвазии.
МРТ является дополнительным методом оценки патологической инвазии плаценты. Значимыми МРТ-предикторами патологической инвазии плаценты являются внутриплацентарные темные полосы на Т2-взвешенном изображении, патологическое выпячивание матки/плаценты, потеря ретроплацентарной линии сигнала низкой интенсивности на Т2-взвешенном изображении, истончение/разрыв визуализации миометрия, прерывистость контуров стенки мочевого пузыря, фокальная экзофитная плацентарная масса и аномальная сосудистая сеть плацентарного ложа. Требуются дальнейшие исследования для определения предикторов патологической инвазии плаценты, расположенной по задней стенке матки.
Перспективы применения метода эластографии в диагностике патологической инвазии плаценты требуют дальнейших исследований.



